Headphone Driver Types Explained

What is a Headphone Driver?
Do you ever wonder what gives your favorite pair of headphones that punchy bass or detailed clarity that you love? If you're a headphone enthusiast, you've likely heard terms like "dynamic," "planar magnetic," and "electrostatic" to describe your favorite cans. But do you know where these names come from? These terms actually derive from the type of driver used in the headphone.
Drivers are small devices inside your headphones that deliver sound to your ears. Each ear cup houses one driver. Drivers transform electrical signals into audible sound waves that are pushed or "driven" to your ears. Think of drivers as miniature speakers.
While each driver type has the same ultimate purpose, they don't all work the same way. Dynamic and planar magnetic drivers, for example, function through the principle of electromagnetism. Electrostatic drivers, meanwhile, function through the principle of static electricity. But all drivers have one thing in common: They produce sound by transforming vibrations into sound waves. Put another way, they convert electrical energy into mechanical wave energy.
A driver is the most essential part of your headphone. It creates the sound that audiophiles hear and love.
Is a Bigger Headphone Driver Better?
Headphone drivers range in size from 20mm to 50mm in diameter. Many people believe the bigger the driver, the better the sound quality -- and manufacturers don't hesitate to tout driver size. So do larger drivers mean better sound quality? In short, no. Generally, a driver’s size determines the loudness of the headphones.
So a bigger driver will mean louder sound -- but not necessarily better sound. This is because headphones with large drivers also tend to struggle in reproducing high frequencies.
Now, a larger diaphragm (the part of the driver that moves air) may give you more powerful and cleaner bass, but again, that's not the entirety of sound quality. There are many factors that come into play when it comes to headphone sound quality, including:
- Technical specs such as impedance and sensitivity
- The type of driver (e.g. dynamic, planar magnetic, electrostatic)
- The tuning of the headphone
- Diaphragm materials (e.g. magnesium, aluminum, beryllium)
- Headphone design (open back headphones vs. closed-back)

Dynamic Drivers
Dynamic drivers (aka moving coil drivers) are the most common and least expensive type of driver. Able to cover the entire frequency range, they are known for great bass response in your music.
Known For: Bass response with a great punch and slam
How it Works:
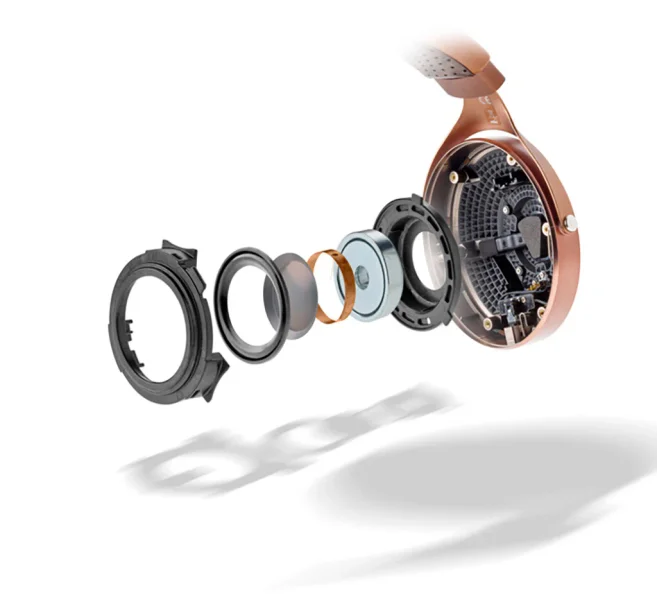
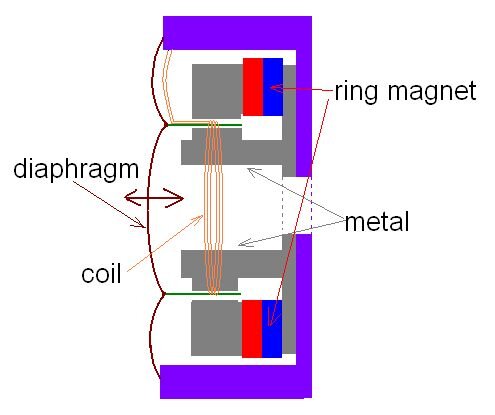
Dynamic drivers include a tiny, stiff, cone-shaped diaphragm connected to a coil of copper wire around a magnet (typically neodymium - a small but very powerful magnet), which magnetizes the coil. When an electrical signal moves through it, the coil creates a magnetic field that causes it to move back and forth (this is why dynamic drivers are also called "moving coil" drivers). Because it is connected to the coil, the diaphragm also moves, displacing the air around it and producing sound.
The substantial amount of air displacement is what gives dynamic drivers a good bass response. The bass can be punchy, fast, and dynamic. EDM and hip-hop in particular are complimented well by dynamic drivers. Also, dynamic drivers usually have vents, which boosts air movement, furthering the bass response.
Advantages
Less expensive, easy to produce
Capable of covering the entire frequency spectrum
Easy to power
Disadvantages
Can distort at high volumes
Loss of detail
The downside to dynamic drivers is that because not all parts of the diaphragm move at the same time, a series of events occur that can cause distortion or loss of resolution–especially at high volumes.
Since dynamic drivers are the most common and affordable driver type on the market, it's no surprise that you'll find them in the cheapest headphones and even some of the most expensive—and the sound quality of the driver itself matches the price tag. For instance, dynamic drivers in high-end headphones use a frameless coil, so the moving piece is much lighter and able to react faster to the signal it's given. Since there is no column that the voice coil fits around, it reduces the overall mass.
Dynamic Headphones
Planar Magnetic Drivers
Planar Magnetic Drivers produce a sound using magnetic fields. Instead of coils though, planar magnetic drivers use a flat, thin diaphragm with wires embedded in it.
Known For: Clear, articulate, lifelike sound with excellent bass
How it Works:
Planar magnetic drivers are similar to dynamic drivers, given both driver types use magnetic fields. However, the difference here is that the diaphragm in a planar magnetic driver has wires embedded in it. This creates an electromagnetic field that can interact with the magnetic field, creating sound waves.
The diaphragm in a planar magnetic driver is sandwiched between two arrays of evenly spaced magnets. An electric current travels through this magnetic field and causes the diaphragm to move, thus producing sound. So it's not the coil that moves the diaphragm; it's the magnets. This is how the name planar magnetic originates -- "magnets acting on a flat plane."
Planar magnetic headphones (also sometimes called orthodynamic) are known for their deep bass response. This is due to a large amount of air that goes through the driver thanks to its large surface area and powerful magnetic force. Another benefit of these drivers is that sound vibrations are evenly distributed across the diaphragm, meaning distortion is minimized.
Advantages
Low distortion
Easy to drive, but they perform best with added power
Disadvantages
Expensive
Larger, heavier
Planar magnetic drivers bring out the detail and clarity in genres like Classical, Blues, and Jazz, as well as vocal-centric songs.
A benefit to planar magnetic drivers is the even distribution of sound vibrations across the diaphragm, creating minimum distortion. You can expect planar magnetic drivers to produce a clear, articulate, lifelike sound with excellent bass.
They can be easy to drive, but they perform best with added power. Take the HiFiMan HE1000SE Headphones for example. These headphones are not as hard to drive as the HiFiMan Susvara Unveiled Headphones but they can really benefit from more power. They will greatly excel in performance the more amplification you can use with them. Given the need for additional power, we recommend pairing your headphones with a Digital Audio Player or DAP, like the Astell&Kern Kann Ultra for portable use.
Planar Magnetic Headphones
Electrostatic Drivers
Of the three most common driver types, Electrostatic Drivers are the most expensive type to manufacture.
Known For: Fast, transparent, detailed, distortion-free sound
How it Works:
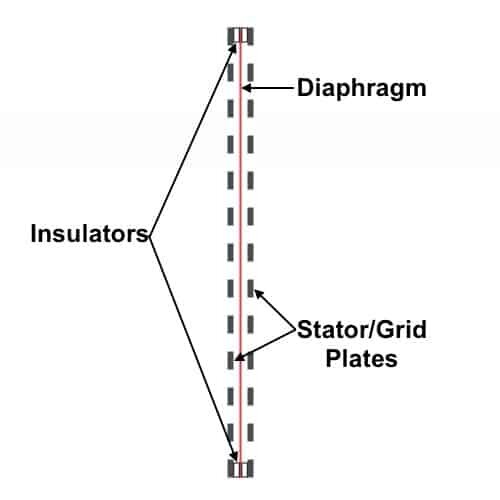
Unlike dynamic and planar magnetic drivers that operate through the principle of electromagnetism, electrostatic drivers work on the principle of static electricity. They contain a thin, nearly weightless diaphragm suspended between two metal plates called stators. These metal plates are perforated to allow airflow. One plate is positively charged and the other is negatively charged.
An electric field is created when a sound signal is applied to the plates. The electric field draws and repels the diaphragm to and from the plates, causing vibrations that push air through the perforations. This, coupled with the continuously charged electrical signal driving the diaphragm, produces sound waves.
Advantages
Small and lightweight
Wide frequency response
Disadvantages
Most expensive
Need special amplifier
Electrostatic drivers are known for supplying excellent detail and treble extension and wide frequency response. You can expect fast, transparent, detailed, distortion-free sound. These drivers are great for genres like acoustic, Americana, and Jazz, as well as any genre where you want great detail retrieval.
Electrostatic headphones must be used with an appropriate electrostatic amplifier or energizer to operate. Not only does this raise the price since they need accompanying hardware most of the time, but it could count them out for portable use. There are a few portable options.
Electrostatic Headphones
Bone Conduction Drivers
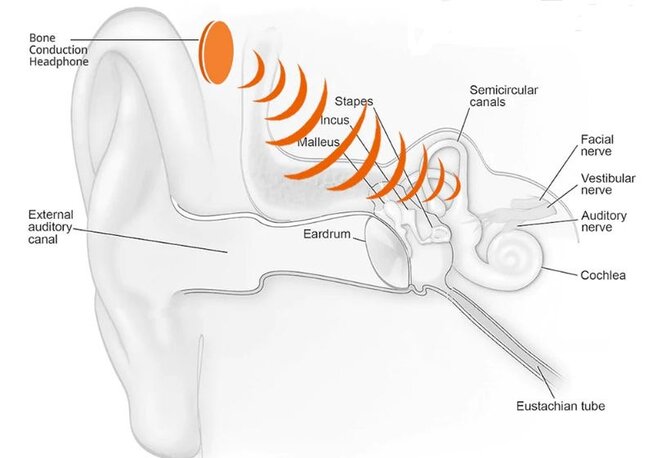
Bone conduction headphones work by transmitting sound vibrations along your cheek and jaw bones instead of through the air.
Known For: Fast, transparent, detailed, distortion-free sound
How it Works:
Bone conduction headphones operate differently than other headphone types. Normally, sound vibrations reach our ears by traveling through the air and down the ear canal, which cause your eardrum to vibrate. Bone conduction headphones work by transmitting sound vibrations along your cheek and jaw bones instead of through the air. In fact, bone conduction headphones sit on your cheek bone. Sound waves bypass the outer and middle ear and travel directly to the cochlea (inner ear).
Bone conduction headphones typically are favored by people with hearing loss stemming from issues in the outer or middle ear, since bone conduction bypasses those parts of the ear. Additionally, because your ear canal is open, you hear ambient sounds, which is good for situational awareness. The downside of bone conduction headphones is they don't have the same level of sound quality as other headphone types.
Advantages
Useful for people with hearing loss
Allows for situational awareness
Disadvantages
Mediocre sound quality; not an Audiophile's choice
Bone conduction headphones provide a level of situational awareness that can be lost with other driver types. Because your ear canal is open, you hear ambient sounds, allowing you to stay tuned into your surroundings. The downside of bone conduction headphones is they don't have the same level of sound quality as other headphone types.
Ribbon Drivers
While primarily used in traditional loudspeakers, ribbon drivers allow for a unique on-the-head use case.
How it Works:
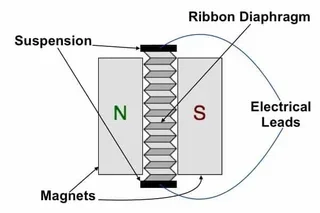
Ribbon drivers feature an ultra-thin and flexible aluminum diaphragm (the "ribbon") suspended between two very powerful magnets. While the ribbon is secured at the top and bottom, it is able to move along its edges. Power from the amplifier is applied across the ribbon, which develops a magnetic field. The field opposes and attracts the adjacent magnets and drives the ribbon evenly over its whole surface. The ribbon moves, pressurizes the air around it, and these sound waves are driven to our ears as music. Low mass and lack of physical suspension are key to ribbon drivers' performance, allowing them to respond to the subtlest of wave formations.
Unfortunately these drivers are not portable and don't offer any noise isolation. With that being said, we don't recommend them to someone who's looking for a pair of headphones to travel with. These headphones are great for a relaxed, at-home listening session.
Advantages
Amazing soundstage and imaging
Details galore
Disadvantages
Not portable, no sound isolation
Special amplification required
Here at Moon Audio, we carry the CA-1A earfield monitor by RAAL Requisite. These are not your ordinary pair of headphones, and like Electrostatic require a special converter box or a dedicated ribbon amplifier to drive them. They require much more power and have a very low impedance that is difficult to control. With the CA-1A you're getting a speaker-like sound from something you wear on your head that weighs less than a pound.
These headphones feature highly specialized ribbon drivers that have a frequency range of 30Hz to 30 kHz in order to eliminate the need for sealed chambered bass and allow for open air baffles for a true full-frequency soundfield.
Ribbon drivers are highly responsive, detailed, and dynamic. Headphone ribbon drivers don't need an enclosure to provide lower bass frequencies. In the case of RAAL's other headphone, the SR1a, you can angle the drivers to give you more or less bass response that you desire. Genres like classic rock, jazz, R&B, and folk pair well with ribbon drivers. This model will provide an even more speaker-like performance.
Ribbon Driver Headphones
FAQ
What is a headphone driver unit?
The driver is the most integral part of your headphone, as it creates the sound that you hear. Drivers transform electrical signals into audible sound waves that are pushed or "driven" to your ears. Think of drivers as miniature speakers. A pair of headphones will feature one driver per ear cup. Dynamic drivers utilize a voice coil, magnets, and a stiff diaphragm, whereas planar magnetic drivers use magnets and a thin diaphragm. Electrostatic drivers feature a thin diaphragm between two metal plates called stators.
What are the six headphone driver types?
The three most common headphone driver types are dynamic, planar magnetic, and electrostatic. Dynamic and planar magnetic drivers function through the principle of electromagnetism. Electrostatic drivers, meanwhile, function through the principle of static electricity. Other driver types include bone conduction; ribbon drivers (mostly found in loudspeakers); and balanced armature drivers (used exclusively in IEMs, aka in-ear monitors or earphones)
Which driver type is best suited for you?
The type of driver used will affect the sound of your headphones. For example, dynamic drivers tend to have good bass response due to the amount of air moved by the driver's diaphragm. Planar magnetic and electrostatic drivers tend to have lower distortion because sound vibrations are evenly distributed across the diaphragm. Dynamic and planar magnetic headphones are going to have better bass response, and electrostatic drivers tend to highlight the higher frequencies. But driver type in and of itself is only one aspect of a headphone's sound. Headphone cup design (open or closed), ear pad material, the materials used in the driver, and the way a headphone is tuned will also have an impact.
Does driver size matter?
Many manufacturers would have you think that a bigger driver automatically means better sound. That's not exactly true. What is true is that a larger diaphragm (the part of the driver that moves air) may produce cleaner, more powerful bass, but may also struggle with higher frequencies. Headphone drivers range in size from 20mm to 50mm, and there are great-sounding headphones at either end of that spectrum. One thing to keep in mind is that the overall mass and thinness of the driver's diaphragm will influence sound quality more than the size of the driver per se. The thinner and lighter the diaphragm, the faster the sound and the lower the distortion.
What is a headphone driver diaphragm?
The diaphragm is the part of the driver that vibrates to create sound waves. Put another way, its job is to convert mechanical vibrations into sounds. Dynamic drivers use larger diaphragms attached to a voice coil. Planar magnetic drivers use large but thin diaphragms, while electrostatic drivers use small, thin diaphragms. In planar drivers, the diaphragm rests between the magnets. In electrostatic drivers, the electrically-charged diaphragm that’s placed between two conductive plates or electrodes. Diaphragms are sometimes called cones, although they are not always cone-shaped. Examples of diaphragm materials are titanium, aluminum, biocellulose and beryllium.
Verdict
Understanding headphone driver types is just one of the stepping stones on the journey to becoming an audiophile. Being able to identify which driver type you'd like in your next pair of headphones can help you make the most informed buying decision. When choosing between driver types, it's important to consider your priorities in terms of sound quality, price, and intended use. Each type has its strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice will depend on your individual needs and preferences. Think about your most-listened to genres, listening scenarios, and price point. Explore our collection of headphones and find your next pair of cans today!
Related Videos
Custom Dragon Audio Cables: How It's Made
How to Pick Your Perfect Pair of Headphones
Open vs. Closed Headphones: What's the Difference?